Records Management Metadata Model
We include this editable document in the Proposal Kit Professional. Order and download it for $199. Follow these steps to get started.
 DOWNLOADABLE, ONE-TIME COST, NO SUBSCRIPTION FEES
DOWNLOADABLE, ONE-TIME COST, NO SUBSCRIPTION FEES
Key Takeaways
- One-time License, No Subscriptions: Pay once and use Proposal Kit forever-no monthly fees or per-use charges.
- Built for Business Projects: Start with a proven Records Management Metadata Model and tailor sections, fields, and branding for your day-to-day project work.
- Instant Access: Download immediately and open the document right away-no waiting, no onboarding delay.
- Project-Ready Structure: Use a ready, professional layout for real-world project tasks (checklists, forms, analysis pages) so teams can execute consistently.
- Fully Editable in Word: Edit everything in Microsoft Word-swap text, add/remove sections, and apply your logo/colors without special skills.
- Step-by-Step Wizard Help: The Proposal Pack Wizard guides you with training/help and keeps you moving-no getting stuck on formatting or assembly steps.
- Wizard Data Merge & Project Management: Let the Wizard manage projects and merge recurring data (company/client names, addresses, dates) across your project documents.
- Included in Proposal Kit Professional: Available exclusively in the Proposal Kit Professional bundle.
 What Our Clients Say
What Our Clients SayAs a freelance consultant, I used Proposal Kit the first time in 2007. Today more than 10 years after, as a CEO of an Intelligence & Influence firm in the military industry, I urge my staff to use the last version of this very useful product. Saving lot of time with professional output."
1. Get Proposal Kit Professional that includes this business document.
We include this Records Management Metadata Model in an editable format that you can customize for your needs.
2. Download and install after ordering.
Once you have ordered and downloaded your Proposal Kit Professional, you will have all the content you need to get started with your project management.
3. Customize the project template with your information.
You can customize the project document as much as you need. You can also use the included Wizard software to automate name/address data merging.
Use cases for this document
Blue Harbor Clinic streamlines records metadata to meet compliance and speed retrieval
The Challenge
Maya Chen, CIO of Blue Harbor Clinic, faced inconsistent metadata across departments, slow document retrieval for auditors, and unclear ownership of patient-related business records in a growing DMS environment that needed to demonstrate regulatory readiness without disrupting clinical operations.
The Solution
The team standardized metadata labels for document title, type, retention date, document status, revision history, project information, and document ownership, and aligned security groups to confidential, restricted, and public categories; Proposal Kit supported the effort by assembling a governance charter, data mapping report, and training plan, while its AI Writer produced supporting materials like a risk assessment and onboarding guides, the RFP Analyzer distilled requirements from a payer's due-diligence request, and line-item quoting packaged implementation and training costs for executive approval.
The Implementation
They piloted with finance and operations, enabled automatic capture of create dates and unique IDs, validated access controls, and used Proposal Kit's document creation tools to publish SOPs, role descriptions, and a self-assessment checklist that tied records retention and access rights to the clinic's business context and audit schedule.
The Outcome
Clinicians and administrators could organize and retrieve record copies in seconds, auditors saw clear traceability and accountability, and leadership approved a clinic-wide rollout, citing faster searches, consistent disposition decisions, and audit-ready document control supported by well-written documentation.
RedLine Fabrication regains control of engineering documents and wins a key OEM contract
The Challenge
Engineering manager Carlos Vega wrestled with CAD files scattered across shared drives, missing revision history, unclear document owners, and frequent mistakes about which drawing was current during production reviews.
The Solution
RedLine implemented a disciplined metadata model in the DMS capturing document type, document status (draft/approved/superseded), revision history, file format and resolution for each digital object, and assigned a document owner for every record; Proposal Kit assembled an engineering metadata standard, change control plan, and communications brief, with the AI Writer creating training handouts and a lessons-learned report, the RFP Analyzer mapping an OEM's information governance requirements to RedLine's controls, and line-item quoting presenting a transparent migration and support estimate.
The Implementation
A staged migration brought drawing libraries under versioned control, automated indexing, tagged designs by project and product line, and Proposal Kit's document creation tools produced concise job aids so teams could describe the content consistently and apply retention dates tied to manufacturing and warranty cycles.
The Outcome
Production errors dropped, engineering reviews accelerated, and the OEM awarded RedLine a multi-year contract after verifying organized, compliant, efficient document control backed by clear policies and implementation evidence.
CivicBright Solutions modernizes municipal records for faster public records responses
The Challenge
Program lead Aisha Patel needed to help a mid-sized city respond to surging public records requests while managing records retention schedules, access rights, and discoverability across Microsoft 365 without risking exposure of restricted information.
The Solution
CivicBright introduced standardized metadata for document title, type, security classification (confidential/restricted/public), retention date, document status, and project information, and configured content types to make records searchable and discoverable; Proposal Kit assembled the proposal, compliance roadmap, and stakeholder briefing deck, the AI Writer created policy summaries and training scripts, the RFP Analyzer extracted obligations from the city's RFP, and line-item quoting detailed phased pricing for configuration, migration, and training.
The Implementation
They configured SharePoint libraries with required fields, automated unique IDs and cutoff dates, published governance SOPs and a self-assessment method using Proposal Kit's document creation features, and trained staff to describe the content consistently and route record copies through approval.
The Outcome
Response times to public requests improved dramatically, departments could retrieve documents reliably, and the city extended CivicBright's contract based on measurable reductions in search time and clear evidence of information governance.
Abstract
This document presents a practical blueprint for managing records metadata in an electronic content management system or document management system. It defines a conceptual model and application profile that treats metadata as data about data, drawn from multiple sources: captured from the record, inherited from a classification scheme, supplied from external databases, or generated automatically at capture. The approach supports managing records across the records lifecycle and enables organized, compliant, efficient operations, considering the situation of the business.
The defined metadata topics and labels map naturally to common categories of metadata. Descriptive metadata includes Document Title and Document Type, populated via a standardized taxonomy and drop-down lists to ensure consistency and searchability. Business-focused types such as Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Budget Management, General Banking Records, Company minute books, Lists/Registers/Logs, and Procurement describe the content and improve discovery.
Administrative metadata covers Author, Unique ID (a document number), Create Date, and Cutoff Date inherited from retention schedules for disposition. Security Group provides access control and security classification (for example, Public or elevated roles), supporting access rights and roles, document control, and audit-ready document control.
Aligned with principles-based standards and guidance such as ISO 23081 and ISO 15489, organizations can use metadata to protect integrity, authenticity, reliability, and usability. Standardised schemas, a standardized metadata schema, and clear information architecture enable indexing, organizing, retrieving, and searching through consistent search fields. Implementation options can include automation tools to automate metadata capture, workflow automation for document review and approval, and version control and audit trails within modern document management systems, aiding regulatory compliance, data governance, and data privacy.
The model is extensible. For born-digital objects and permanent electronic records, preservation and technical metadata can be added for long-term preservation: file format, file size, checksum or fixity value, digital signatures, encryption algorithm, and PREMIS-aligned preservation metadata. Structural metadata that captures content, context, and structure helps create access copies and strengthens traceability and discovery. These best practices apply across record environments, including Microsoft 365 deployments and engineering document management.
Use cases include finance teams managing general accounting records, procurement files, and tax records; corporate secretariat records; and digital communications requiring access controls, retention policies, and document retrieval. Records managers and information managers can employ a self-assessment checklist to validate managing metadata for records against regulations and standards.
Proposal Kit can help produce the supporting policy documents and metadata schema definitions using its document assembly, extensive template library, and AI Writer to write related guidance and self-assessment materials, while automated line-item quoting streamlines proposals for implementation projects. This supports consistent, business-ready documentation that is easy to use.
Expanding on the model, organizations should define clear metadata labels that cover administrative, descriptive, technical, and preservation needs. Beyond fields that describe the content, add document status, revision history, project information, document ownership, and a document owner, plus a record copy flag to separate authoritative versions from reference copies. Include a retention date linked to records retention schedules to support regulatory requirements.
For each digital object, technical details such as file format and resolution help organize, retrieve, and ensure accessibility and discoverability. Security categories like confidential, restricted, and public guide access rights in a DMS while preserving integrity, authenticity, reliability, and usability across information life cycles.
A principles-based standard helps resolve conceptual and implementation issues by mapping categories of metadata to business context and information governance controls. A self-assessment method lets records managers test compliance and data protection readiness, confirm that content is searchable and discoverable, and verify indexing, organizing, and retrieval performance. Marking document status and revision history strengthens audit readiness and traceability, while project information connects records to operations.
Identifying a document owner clarifies accountability for updates and disposition. Labeling the record copy avoids confusion, and using consistent metadata labels across the DMS supports organised, compliant, efficient practices for document review and approval, and document control.
Proposal Kit fits this scenario by assembling the proposal, policies, and schema documentation needed to configure metadata labels and categories, produce a self-assessment checklist, and document DMS configuration and project plans. Teams can use its AI Writer and template library to write guidance aligned to regulatory requirements, while automated line-item quoting helps price implementation work. This speeds delivery of coherent, usable documentation that supports indexing, organizing, retrieval, and long-term governance.
Further strengthening the approach, teams should design capture forms that guide users with plain-language prompts and examples for each field that describe the content. Clear metadata labels, defined field lengths (for example, 250 characters for titles and types, 15 for a unique ID, and 60 for a security group), and controlled drop-downs reduce errors and improve consistency. Helpful tooltips can distinguish Create Date from Cutoff Date and retention date, and clarify how document status (write, approved, superseded) and revision history support auditability.
Mapping security groups to confidential, restricted, and public improves access control without slowing work. Align search facets in the DMS to high-value fields-Document Type, Project Information, Document Ownership, and Author- so that records become more searchable and discoverable.
A pragmatic implementation plan starts with a pilot that exercises ingestion of a representative digital object set, validates indexing, organizing, and retrieval, and confirms that the application profile meets regulatory requirements. Define stewardship roles for each metadata topic (for example, a document owner who maintains accuracy), plus quality checks for completeness, format, and pick-list use. Establish metrics such as metadata completeness rate, exception counts, and time-to-retrieve to demonstrate organised, compliant, and efficient outcomes.
During migration, perform metadata remediation to normalize values, reconcile record copy flags, and attach retention schedules. Schedule periodic self-assessment against a principles-based standard to surface conceptual and implementation issues early and keep information governance aligned with business context and information life cycles.
Proposal Kit can streamline this work by assembling governance charters, SOPs, training guides, and configuration narratives that explain what each field captures and how it describes the content. Its templates and AI Writer help produce checklists, implementation plans, and role definitions, while automated line-item quoting supports scoping and pricing the rollout. This accelerates delivery of coherent documentation that supports consistent capture, effective search, and durable compliance.
How do you write a Records Management Metadata Model document?
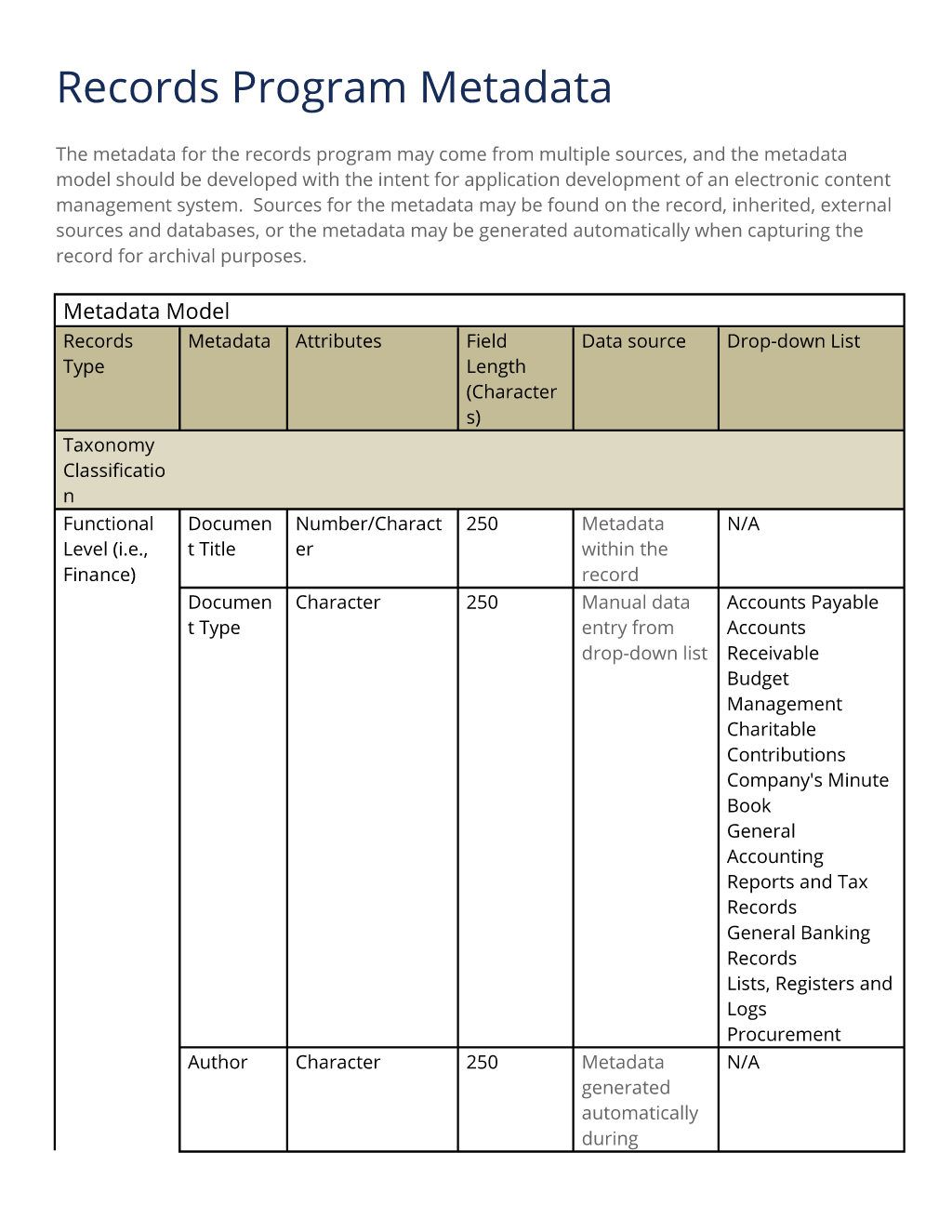
Records Program Metadata
The metadata for the records program may come from multiple sources, and the metadata model should be developed with the intent for application development of an electronic content management system. Sources for the metadata may be found on the record, inherited, external sources and databases, or the metadata may be generated automatically when capturing the record for archival purposes. Metadata Model Records Type Metadata Attributes Field Length. Data source Drop-down List Taxonomy Classification Functional Level (i.e., Finance) Document Title Number/Character 250 Metadata within the record N/A Document Type Character 250 Manual data entry from drop-down list Accounts Payable.
Accounts Receivable
Budget Management
Charitable Contributions
Company's Minute Book
General Accounting Reports and Tax Records.
General Banking Records
Lists, Registers and Logs
Procurement Author Character 250 Metadata generated automatically during capture of the record N/A Unique ID Number 15 System generated, map defined metadata attributes, specific business and/or technical requirements N/A Create Date Date 10 System generated N/A Cutoff Date Date 10 Metadata inherited from the records classification scheme for disposition N/A Security Group Character 60 Metadata provided by user details according to the user's log on Public.
Super User
The editable Records Management Metadata Model document - complete with the actual formatting and layout is available in the retail Proposal Kit Professional.
20% Off Discount
 4.7 stars, based on 849 reviews
4.7 stars, based on 849 reviewsRelated Documents
- Records Survey and Inventory Analysis
- Records Management Taxonomy Topic Template
- Records Management File Plan Template
- Records Management Expanded File Plan Template
- Records Inventory Worksheet
- Records Access Security Plan (Expanded)
- Communication Plan
- RACI Matrix Worksheet
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT) Schedule
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT) Enhancements and Bug Tracker
- Risk Mitigation Plan
 Ian Lauder has been helping businesses write their proposals and contracts for two decades. Ian is the owner and founder of Proposal Kit, one of the original sources of business proposal and contract software products started in 1997.
Ian Lauder has been helping businesses write their proposals and contracts for two decades. Ian is the owner and founder of Proposal Kit, one of the original sources of business proposal and contract software products started in 1997.By Ian Lauder
 Published by Proposal Kit, Inc.
Published by Proposal Kit, Inc.We include a library of documents you can use based on your needs. All projects are different and have different needs and goals. Pick the documents from our collection, such as the Records Management Metadata Model, and use them as needed for your project.



 Cart
Cart
 Get 20% off ordering today:
Get 20% off ordering today:  Facebook
Facebook YouTube
YouTube Bluesky
Bluesky Search Site
Search Site